Selection Stainless Steel for Handling Sulphuric Acid H2SO4
Sulphuric acid is oxidising when concentrated but is reducing at low and 'intermediate' concentration.
The response of most stainless steel types is that in general they are resistant at either low or high concentrations, but are attacked at intermediate concentrations. Commercially concentrated acid is around 96 wt % (sg = 1.84)
The improvement in corrosion resistance moving from 304 /1.4301 to 316 / 1.4401 is due to the addition of molybdenum.
Further additions of moybdenum and copper in the 1.4539 904L grade extend the corrosion resistance in these reducing acid conditions.
The molybdenum in types 316 and grade 1.4539 also helps improve resistance to chloride attack, when present as impurities in the acid.
Material performance in Sulphuric acid, H2SO4
| Conc. % |
20 |
20 |
20 |
20 |
30 |
30 |
30 |
30 |
40 |
40 |
40 |
40 |
50 |
50 |
50 |
| Temp. °C |
50 |
60 |
80 |
100 |
20 |
40 |
60 |
80 |
20 |
40 |
60 |
90 |
20 |
40 |
70 |
| Grade or type of alloy: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Carbon steel |
2 |
2 |
|
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
|
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
| 13 Cr |
2 |
2 |
|
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
|
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
| 304/304L |
2 |
2 |
|
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
|
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
| TP316/316L |
1 |
2 |
|
2 |
1 |
2 |
2 |
|
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
| 18Cr13Ni3Mo/317L |
1 |
1 |
|
2 |
1 |
1 |
2 |
|
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
| 17Cr14Ni4Mo / 1.4439 |
1 |
1 |
|
2 |
1 |
1 |
2 |
|
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
| 904L / N08904 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
2 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
|
0 |
0 |
1 |
2 |
0 |
0 |
2 |
| Sanicro 28 |
0 |
0 |
|
2 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
|
0 |
0 |
1 |
2 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
| 254 SMO |
0 |
0 |
|
2 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
2 |
|
1 |
|
|
0 |
1 |
|
| 654 SMO |
0 |
0 |
0 |
2 |
|
|
|
|
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
0 |
0 |
|
| SAF 2304 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
| SAF 2205 |
0 |
1 |
2 |
2 |
0 |
1 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
| SAF 2507 |
0 |
0 |
|
|
|
0 |
1 |
|
0 |
|
|
2 |
|
|
2 |
| Titanium (CP Ti) |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
| SAF 2906 |
|
|
0 |
2 |
|
|
|
2 |
|
0 |
2 |
|
2 |
2 |
|
| SAF 2707 HD |
|
|
0 |
2 |
|
|
|
2 |
|
0 |
0 |
|
2 |
2 |
|
| SAF 3207 HD |
|
|
0 |
2 |
|
|
|
2 |
|
0 |
0 |
|
0 |
2 |
|
|
| Conc. % |
60 |
60 |
60 |
70 |
70 |
70 |
80 |
80 |
80 |
85 |
85 |
85 |
85 |
90 |
90 |
| Temp. °C |
20 |
40 |
70 |
20 |
40 |
70 |
20 |
40 |
60 |
20 |
30 |
40 |
50 |
20 |
30 |
| Grade or type of alloy: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Carbon steel |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
0 |
1 |
2 |
2 |
0 |
1 |
| 13 Cr |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
1 |
1 |
2 |
2 |
0 |
1 |
| 304/304L |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
2 |
0 |
0 |
| TP316/316L |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
1 |
2 |
2 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
2 |
0 |
0 |
| 18Cr13Ni3Mo/317L |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
1 |
2 |
2 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
2 |
0 |
1 |
| 17Cr14Ni4Mo / 1.4439 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
1 |
2 |
2 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
2 |
0 |
1 |
| 904L / N08904 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
2 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
| Sanicro 28 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
|
1 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
| 254 SMO |
0 |
1 |
|
0 |
1 |
|
0 |
1 |
2 |
0 |
|
|
|
1 |
|
| 654 SMO |
0 |
1 |
|
0 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
| SAF 2304 |
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
1 |
|
|
|
1 |
| SAF 2205 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
1 |
|
|
2 |
2 |
2 |
1 |
|
|
|
1 |
1 |
| SAF 2507 |
|
|
|
0 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
|
2 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
|
0 |
0 |
| Titanium (CP Ti) |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
| SAF 2906 |
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
1 |
2 |
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
| SAF 2707 HD |
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
2 |
2 |
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
| SAF 3207 HD |
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
2 |
2 |
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
| Conc. % |
90 |
90 |
94 |
94 |
94 |
94 |
96 |
96 |
96 |
96 |
98 |
98 |
98 |
98 |
| Temp. °C |
40 |
70 |
20 |
30 |
40 |
50 |
20 |
30 |
40 |
50 |
30 |
40 |
50 |
80 |
| Grade or type of alloy: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Carbon steel |
2 |
2 |
0 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
0 |
1 |
2 |
2 |
1 |
1 |
2 |
2 |
| 13 Cr |
2 |
2 |
0 |
1 |
2 |
2 |
0 |
1 |
2 |
2 |
1 |
1 |
2 |
2 |
| 304/304L |
2 |
2 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
2 |
2 |
| TP316/316L |
1 |
2 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
2 |
| 18Cr13Ni3Mo/317L |
1 |
2 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
2 |
| 17Cr14Ni4Mo / 1.4439 |
1 |
2 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
2 |
| 904L / N08904 |
1 |
2 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
2 |
| Sanicro 28 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
| 254 SMO |
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
2 |
| 654 SMO |
2 |
2 |
|
|
|
2 |
0 |
1 |
|
2 |
|
|
1 |
1 |
| SAF 2304 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
0 |
|
|
0 |
1 |
| SAF 2205 |
1 |
|
0 |
|
|
|
0 |
0 |
1 |
|
0 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
| SAF 2507 |
0 |
2 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
| Titanium (CP Ti) |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
| SAF 2906 |
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| SAF 2707 HD |
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| SAF 3207 HD |
|
2 |
|
| Conc. H2SO4 % |
100 |
100 |
100 |
100 |
100 |
100 |
| Conc. SO3 % |
7 |
11 |
11 |
60 |
60 |
60 |
| Temp. °C |
60 |
60 |
100 |
20 |
70 |
80 |
| Grade or type of alloy: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Carbon steel |
0 |
0 |
2 |
|
|
|
| 13 Cr |
0 |
0 |
2 |
|
|
2 |
| 304/304L |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
| TP316/316L |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
| 18Cr13Ni3Mo/317L |
0 |
0 |
|
0 |
0 |
|
| 17Cr14Ni4Mo / 1.4439 |
0 |
0 |
|
0 |
0 |
|
| 904L / N08904 |
0 |
0 |
|
0 |
0 |
|
| Sanicro 28 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 254 SMO |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 654 SMO |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| SAF 2304 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| SAF 2205 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| SAF 2507 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Titanium (CP Ti) |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
Symbol clarification
These corrosion tables use a number of symbols, having the following meanings:
| Symbol |
Description |
| 0 |
Corrosion rate less than 0.1 mm/year. The material is corrosion proof. |
| 1 |
Corrosion rate 0.1—1.0 mm/year. The material is not corrosion proof, but useful in certain cases. |
| 2 |
Corrosion rate over 1.0 mm/year. Serious corrosion. The material is not usable. |
| p, P |
Risk (severe risk) of pitting and crevice corrosion. |
| c, C |
Risk (Severe risk) of crevice corrosion. Used when there is a risk of localised corrosion only if crevices are present. Under more severe conditions, when there is also a risk of pitting corrosion, the symbols p or P are used instead. |
| s, S |
Risk (Severe risk) of stress corrosion cracking. |
| ig |
Risk of intergranular corrosion. |
| BP |
Boiling solution. |
| ND |
No data. (Used only where there are no actual data to estimate the risk of localised corrosion instead of p or s). |
Corrosion resistance of stainless steel
In the following iso-corrosion diagrams, each line shows the 0.1mm/year corrosion rate. This is usually regarded as the boundary between acceptable and unacceptable performance. (The broken line represents the boiling point)
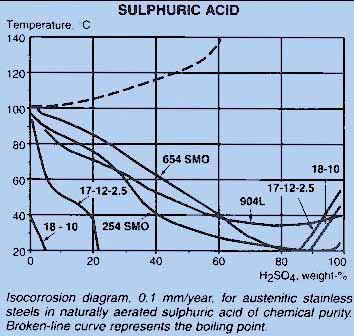
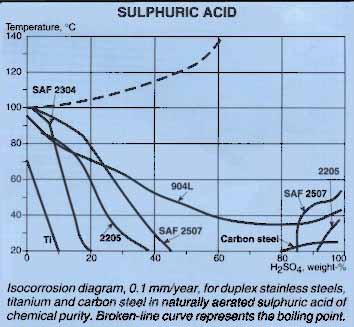
Comments on Specific Grades
18-10 (1.4301, 304) - limited use in dilute acids 5% maximum at room temperature. Increasing temperature quickly makes the steel useless. Acceptable above about 90% at room temperature.
17-12-2.5 (1.4401, 316) - This grade offers a significant advantage over 304 at low concentrations, up to 22% at room temperature only gradually falling with temperature up to 40 deg C and then more quickly to about 5% at 60 deg C.
Duplex Steels - 2304 (1.4362) is similar to 1.4401 (316) at room temperature but only gradually falls off with temperature, still allowing about 8% at 80 deg C. 1.4462 (2205) is acceptable to as high 40% at room temperature falling to about 12% at 80 deg C. Superduplex 2507 (1.4410) offers only limited improvement to 45% at room temperature.
904L (1.4539) - This steel was specifically developed for sulphuric acid use and van be used across the whole concentration range up to 35 deg C.
Concentrated Acids
Care needed with very concentrated (98-100%) acid at higher temperatures as slight changes to the conditions that help resistance ie the high concentration falling by dilution.
Increases in velocity or reductions in oxidising conditions, can affect the corrosion resistance anticipated.
Impurities
he presence of chlorides in sulphuric acids can be an additional hazard.
Hydrochloric acid (HCl) can be liberated from sodium chloride by sulphuric acid, depending on the temperature, making the mixture more aggressive.
Influence of alloy additions to stainless steels on corrosion resistance
The alloying addition of copper is most beneficial to extending the resistance of stainless steel in intermediate concentrations of sulphuric acid.
Duplex stainless steel containing copper, such as grade 1.4501 can also be considered for sulphuric acid service.
Silicon stainless steels such as grade 1.4361 should be considered for hot, very concentrated acid applications.
Risk of corrosion from 'self-dilution' of sulphuric acid
Sulphuric acid has a strong affinity for water, extracting water from its surroundings and hence diluting itself.
The result can be that acid thought to be 'safely' concentrated for contact with 304 type stainless steels, say above 90%, can actually attack the steel if water has been picked up.
This can occur in open topped containers where moisture from the air dilutes the acid and results in corrosion around the 'liquid-line'.
The resistance of stainless steels also depends on temperature.
As heat is generated when the acid is diluted warmer conditions can be present locally, which can add to the risk of attack in the diluter acid.
The sensitivity to temperature can also be a hazard at 'hot wall' effects in heating circuits or with heat exchanger elements.
Affect of aeration and oxidising conditions
Aeration or the presence of oxidising 'agents' in sulphuric acid contributes to the corrosion resistance of stainless steels.
Stainless Steels have lower resistance to de-aerated sulphuric acid. Reducible ions such as Fe3+, Cu2+, Sn4+ are effectively oxidising agents and can reduce corrosion if present in the acid.
Similarly oxidizing agents like chromic or nitric acid reduce corrosion rates, if present in the sulphuric acid.
Dissolved sulphur trioxide (SO3) present in sulphuric acid over 97% concentrations, can also reduce corrosion rates.
Chromium content is important to the resistance of the steel and so 310 can be considered when oxidising agents are present, making use of the extra chromium (25%).
The moderately oxidising conditions in dilute sulphuric acid can result in localised intercystalline attack (ICC), especially if the chromium is locally reduced, as is the case when 'standard' carbon 304 or 316 types are 'sensitised'.
This why the 304L types, or the stabilised types such as 321, are used where weld heat affected zone (HAZ) areas cannot be re-solution heat-treated.
It is important to be careful with corrosion data, as small variations in impurities or conditions can affect service corrosion rates and hence potential durability of stainless steels in sulphuric acid.
Affect of velocity of flow
Stainless steels are more suitable than carbon steels for handling high flow rates of concentrated acid (90-98%). The passive layer on stainless steels is more stable than the ferrous sulphate layer formed on carbon steel in turbulent flow conditions. Flow rates can become a problem as the active/passive region of concentration and temperature is approached.
Use of stainless steels in contact with battery acid
Battery Acid is sulphuric acid with a weight percentage concentration of over 35 i.e. at a 'fully charged' specific gravity of 1.28. The selection of 304 or 316 types for applications involving prolonged contact, such as storage tanks, is not advisable. A concentration limit of 22% maximum at 20 degC can be taken for 316, from the iso-corrosion diagram.
For storage applications or where either long plant service life or safety considerations are important, 'battery' concentration sulphuric acid, austenitic grades such as 1.4539 or 1.4563 should be considered.
The 316 types may be suitable for applications involving short term or intermittent contact such as battery disposal plant or spillage trays. As this application is a 'borderline' case, care should be taken to ensure that the acid concentration is not allowed to increase through water evaporation (drying out) and that temperatures are maintained as low as possible
Releated References:
Selection of Stainless Steel fo Handling Sulphur Dioxide SO2 and Sulphur Trioxide SO3
Selection of Stainless Steel for Handling Phosphoric Acid H3PO4
Selection of Stainless Steel for Handling Hydrofluoric Acid HF
Selection of Stainless Steel for Handling Citric Acid C3H4OH (COOH)3
Selection of Stainless Steel for Handling Ammonia NH3
Selection of Stainless Steel for Handling Chlorine Cl2 and Chlorine Dioxide ClO2
Selection of Stainless Steels For Handling Hydrochloric Acid HCl
Selection of Stainless Steel for Handling Sulphuric Acid H2SO4
Selection Stainless Steel for Handling Sodium Hydroxide NaOH
Selection of stainless steels for handling acetic acid (CH3COOH)
Selection of stainless steels for handling sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl)
Selection of stainless steels for handling nitric acid (HNO3)
NACE MR 0175/ISO 15156 for Corrosion Resistant Alloys for Sulphide Service
Selection of stainless steels in water supply and waste water treatment
|
