Avoiding Galvanic Corrosion
When selecting components for your cooling loop, you must consider their material compatibility as well as their individual performance. Although an aluminum cold plate paired with a copper heat exchanger tube might meet your thermal requirements, it is not a reliable cooling circuit. Copper and aluminum have widely different electrochemical potentials, so when they are combined in a cooling system, galvanic corrosion is likely. Galvanic corrosion (also called dissimilar metal corrosion) erodes the metal, causing leaks over time.
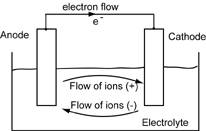
In a cooling loop, metallic materials in electrochemical contact can form a galvanic cell, or battery (fig. 1). In a galvanic cell, when two metals with different electrical potentials are connected, there is a potential difference across them. The metal with the higher electrical potential becomes the anode, and the lower, the cathode. A current will flow from the anode to the cathode. The anode dissolves, or corrodes, to form ions. These ions drift into the water where they either stay in solution or react with other ions in the electrolyte. This process is known as galvanic corrosion.
A galvanic cell requires three elements:
- Two electrochemically dissimilar metals,
- An electrically conductive path between the two metals, and
- An electrolyte to allow the flow of metal ions.
In a typical liquid cooling circuit, the plumbing provides the electrically conductive path, and the aqueous coolant provides the electrolyte. In the copper/aluminum scenario mentioned above, the aluminum is the anode, the copper is the cathode and the cooling fluid is the electrolyte. Over time, the aluminum corrodes as it dissolves into the water.
The galvanic corrosion rate depends on the electrical potential between the two metals. The Galvanic Series (fig. 2) orders metals based on the potential they exhibit in flowing seawater. The most reactive are at the top of the table, and the least reactive at the bottom. 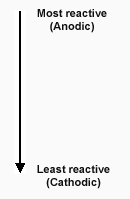
Fig 2. Galvanic Series*
- Magnesium
- Zinc
- Aluminum (most types)
- Iron, plain carbon and low alloy steels
- Lead, high lead alloys
- Tin plate, tin/lead solder
- Chromium plated materials, chromium alloys, chromium type-steels
- Brass
- Copper
- Nickel
- Stainless steel
- Silver
- Gold
Elevated temperatures, which are likely in cooling loops, accelerate galvanic corrosion. A 10°C increase in temperature can approximately double the corrosion rate. Corrosion inhibitors can be added to the cooling water. This retards, but does not eliminate, galvanic corrosion. Corrosion inhibitors bind with the ions in solution to neutralize them. The inhibitors are consumed in this process so they need replacing regularly. Non-aqueous coolants, such as oils, eliminate galvanic corrosion because they do not support ions. However, thermal performance is sacrificed, as the thermal conductivities of heat transfer oils are generally significantly lower than water-based coolants.
To avoid galvanic corrosion, we highly recommend using the same materials, or materials with similar electrical potential, throughout your cooling loop. You should ensure that the plumbing, connectors and other components do not introduce a reactive metal into the system.
Using the same materials throughout your circuit does not mean that you have to sacrifice performance. Offers high performance heat exchanger and cold plates with aluminum, copper and stainless steel fluid paths.
|
