Bi-Metallic Corrosion Galvanic Corrosion
Bi-Metallic corrosion Galvanic Corrosion is the additional corrosion that occurs when dissimilar metals are in contact in the presence of an electrolyte. The corrosion of a metal, the anode, results from the positive current flowing from the anode to the less reactive (more noble) metal, the cathode, through the electrolyte.
This process is similar to the conventional corrosion of a single, uncoupled metal but generally proceeds at a higher rate depending on the difference in electrochemical reactivity of the anode and cathode metal.
The requirements for bi-metallic corrosion are as follows:
- An electrolyte bridging the two metals
- Electrical contact between the two metals.
- A difference in potential between the metals to enable a significant galvanic current
- A sustained cathodic reaction on the more noble of the two metals.
Electrolyte
The degree of bi-metallic corrosion is affected by the electrolyte pH and conductivity. The intensity of the corrosion can increase with the conductivity of the electrolyte. Typical values of conductivity of various fluids are listed below;
| Distilled Water |
0.5-2 μS/cm |
| Stored Distilled Water |
2-4 μS/cm |
| Supply Water |
50-1500 μS/cm |
| Sea Water |
50,000 μS/cm |
| Sat. Sodium Chloride |
250,000 μS/cm |
| Sulphuric Acid |
up to 800,000 μS/cm |
Bi-metallic corrosion is seldom a problem when the metals are immersed in pure water.
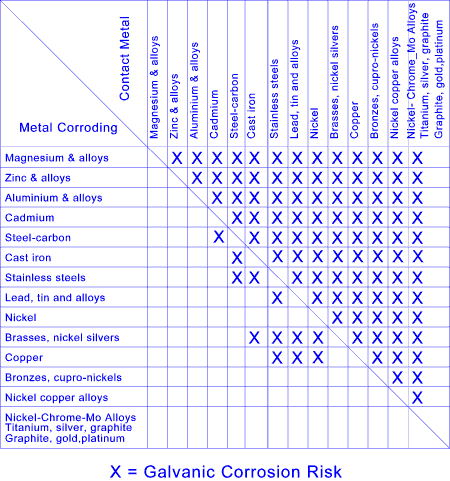
Methods of Reducing Corrosion resulting from Galvanic Corrosion
Where contact between dissimilar metals cannot be avoided the following steps should be considered
- Select metals that are close together in the galvanic series for the relevant environment
- Avoid relatively small areas of the less noble metal and large areas of the more noble metal
- Insulate the metals from each other
- Exclude electrolyte from around the bimetallic junction e.g painting
- Paint both metals where possible: if impractical paint the most noble metal
- Provide additional corrosion allowance on the less noble metal
- Apply compatible metal or sacrificial metal coatings
- If electrical insulation is used to minimise the risk, then test for the insulation quality as part of maintenance regime
Galvanic Series
Reference Oxidation Reduction
Galvanic corrosion is driven by the voltage potential between two electrically connected conductors ( To minimize this form of attack, materials in electrical contact, if required, should be selected so as to minimize their relative potential.
The galvanic series of metals lists common materials in order of their electrical potential relative to a recognized standard. Materials widely separated on this list will rapidly corrode in the presence of electolyte (e.g. Seawater) when in electrical contact, the anodic material suffering rapid material loss. Materials close together on this list will suffer less damage due to corrosion.
- Anodic - Least Noble
- Magnesium
- Magnesium Alloys
- Zinc
- Cadmium
- Aluminum
- Mild Steel , Wrought Iron
- Cast Iron, Low Alloy High Strength Steel
- Chrome Iron (active)
- Stainless Steel, 430 Series (active)
- Stainless Steel 302, 303, 321, 347, 410,416, (Active)
- Ni - Resist
- Stainless Steel 316, 317, (Active)
- Aluminum Bronze
- Hastelloy C (active) Inconel 625 (active)
- Titanium (active)
- Lead - Tin Solders
- Lead
- Tin
- Inconel 600 (active)
- Nickel (active)
- Hastelloy B (active)
- Brasses
- Copper
- Manganese Bronze , Tin Bronze (
- Nickel Silver
- Copper - Nickel Alloy 90-10
- Copper - Nickel Alloy 80-20 s
- Stainless Steel 430
- Nickel, Aluminum, Bronze
- Monel
- Silver Solder
- Nickel (passive)
- 60 Ni- 15 Cr (passive)
- Inconel 600 (passive)
- 80 Ni- 20 Cr (passive)
- Chrome Iron (passive)
- Stainless Steel 302, 303, 304, 321, 347,(PASSIVE)
- Stainless Steel 316, 317,(PASSIVE)
- Incoloy 825nickel - Molybdeum - Chromium
- Iron Alloy (passive)
- Silver
- Titanium (pass.) Hastelloy C (passive)
- Inconel 625(pass.)
- Graphite
- Zirconium
- Gold
- Platinum
|
