Corrosion of Piping
A significant proportion of the corrosion problems experienced relate to piping systems. Piping systems are used to transfer a wide range of fluids in a wide range of environments.A major lifetime costs for any industrialised plant is the cost of leaking fluids and the cost of repair of piping system to prevent and eliminate leaks. The main methods of preventing corrosion in piping systems are as follows;
Selection of materials
Corrosion resistant surface coating
Location /Geometry of piping systems
Cathodic protection methods
Piping Materials
There is an extremely wide range of pipeline materials available. These are selected on various criteria the two most important of which are suitability for service and cost. The suitability for service is determined primarily on the materials resistance to attack by the fluid being transferred and the external environment. The internal corrosion resistance is more important than the external resistance. It is easier to protect and monitor and repair the external surfaces. Also the environment generally provides a less arduous regime.
Carbon Steel
Material containing no principle alloying elements. Piping useable up to 430oC. Widely used and design requirements are detailed in all relevant codes. Corrosion allowed for when necessary by applying corrosion allowances.
Low Alloy Steel
Material contains small percentages (less than 3%) of alloying elements such as chromium, nickel, molybdenum or vanadium. The material has higher temperature range compared to carbon steel.
A typical range of fluids with suitable pipeline materials is listed below:
| Fluid |
Pipe line material |
| Process Air |
Carbon Steel, Copper, Plastic |
| Potable Water |
Carbon Steel, Copper, Plastic |
| Low Pressure Sat.Steam |
Carbon Steel, Copper |
| High Pressure Dry Steam |
Carbon Steel |
| Demineralised Water |
304 Stainless Steel, |
| Seawater |
304/316 Stainless steel, Aluminium Bronzes, Copper nickel alloys, Nickel alloys, Superduplex, 6%(or7%)Mo St. steels, Duplex steel, Titanium |
| Nitric Acid |
304 Stainless Steel |
| Nitrogen, |
Carbon Steel, |
| Argon |
Carbon Steel, |
| Instrument Air |
Carbon Steel, |
Stainless Steel
Steels specifically alloyed for corrosion resistance generally with chromium levels above 18%. Steels resist oxidisation and specific corrosion of virtually all chemicals over a wide temperature range (-200oC to 900oC ). The corrosion resistance is related to the grade selected. Stainless steels are represented in all design codes and are convenient to use. Stainless steel generally costs a least 4 times more than carbon steels.
Cast Iron /Ductile Iron
Two types of cast iron are used, grey cast iron and ductile iron. The former includes graphite as flakes and the latter includes graphite in spherical or nodular form. Cast iron piping has been widely used over the years for transferring a wide range of fluids as it is a low cost option with excellent corrosion resistance to a wide range of environments and fluids. The grey cast irons are generally being superseded by the ductile iron options and the ductile iron piping systems are now being generally replaced by plastic piping. The British Standard for Ductile piping and fittings is BS 4772.
Lead has been used in the past for a wide variety of domestic, civil and chemical piping. It is suitable for most chemicals it is readily available and easily worked. Although lead is expensive it is can be totally recovered and reused. Lead has low strength properties and suffers from creep. It can be alloyed to improve the strength and creep resistance. Lead is no longer used for domestic piping for human health reasons. Lead not widely used now because plastic piping provides improved properties at lower costs.
Copper, Brass, Copper Nickel Alloys
Piping and tubing made from these metals are used for many purposes throughout industry and also for building and domestic use and for ship pipework engineering because of the resistance of the brasses to sea water attack. Copper and the associated metals generally conform to the relevant standards and are therefore conveniently produced and installed.
- Copper tubing is used where ease of fabrication is important.
- 70%/30% - Cu/Zn brass is a good general purpose material used for a variety of applications e.g. heat exchanger tubes, and closed circuit systems.
- Admiralty brass 70% /1%/29% - Cu/Sn/Zn has slighty improved resistance to polluted water compared to 70/30 brass.
- Brass with 76%/2%/0,04%- Cu/Al/As and Remainder Zn has good resistance to seawater attack and is used for diverse process plants for transferring seawater under turbulent conditions to resist corrosion and impingement attack.
- Cupro Nickel Containing 31%/2% - Ni/Fe and " Kunifer" containing 10.5%/1.7% - Ni/Fe are also used for transferring seawater and high good strength at elevated temperatures.
Aluminium / Aluminium Alloys
Aluminium piping is supplied in two grades to BS 1471: 1972 . Aluminium is used in many industries and provides excellent corrosion resistance compared to steel for arduous fluid flow applications.
Glass and Glass Lined piping
Glass piping and glass lined piping provides ideal corrosion resistance to most fluids. However this material is not coveniently installed and has various mechanical limitations. It is used mainly for specialised application including laboratories.
This material has only recently been available in quantity. At this time it is relatively expensive compared to most other materials. However if lifetime costing is consided it would likely be competitive as it has superb corrosion resistance especially for seawater transfer duties. When installed in seawater systems titanium piping provides long continuous service compared to virtually all other metals.
Elastomer/Plastic Lined Steel Piping
This option provides a relatively low cost method of producing a highly corrosion resistant piping system with good mechanical properties. However if system design, manufacture and installation is not good the lining system may fail resulting in high rates of local corrosion and expensive early repairs.
Piping systems made from plastics including HDPE, ABS, PVC etc. are not subject to the same corrosion problems experienced by metal piping systems. More and more piping systems are being manufactured from plastics. However plastics have severely limited mechanical mechanical and thermal properties and are attacked by some chemicals.
This area of design is discussed on separate page Surface coatings
Location/Geometry of piping systems
The life of a piping system can be significantly improved if the system is correctly designed in respect to geometry and location. The piping should be designed to ensure that there are no low points which are not fully drained. The piping should also be located to minimise the risk of attack from the environment. If possible piping should be protected against environments hich include excessive precipitation in industrial or marine areas.
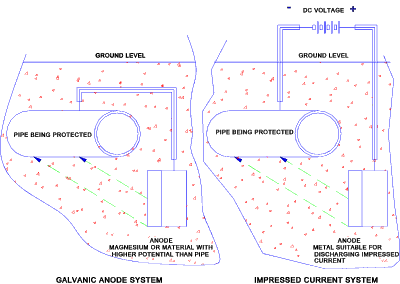
Galvanic anode system
Buried ferrous or cast iron piping, however well protected cannot be fully isolated from the moist soil and will therefore be at risk of corrosion. Corrosion will occur where the base metal comes into contact with the salts in the ground with the presence of water. The base metal will behave as an anode. Cathodic protection involves forcing the buried pipe to become a cathode relative to a buried electrode which will act as an anode. This involves connecting the pipe using an insulated cable, to a buried bar made from magnesium or other metal with a similar electric potential relative to the pipe material. As the buried electrode is electrically positive compared to the pipe this forces the pipe to be a cathode. The buried bar acts as a sacrificial anode. The pipe therefore acts as a cathode and is not corroded.
The sacrificial anodes are buried about 3m from the pipe and are pitched at about 250m. The anodes are generally engineered to have a life expectancy of upto ten years.
Impressed Current System
A similar level of protection can be provided by applying a generated DC voltage across the pipe and a buried buried electrode from cast iron or some similar low cost metal which can discharge a current to the soil. The applied voltage forces the buried electrode to be positive relative to the pipe ensuring that it will behave as an anode
Cathodic protection systems require specialised design involvement.
Metallographic Test - Metallography Testing
Metallographic Test Report
Stress Corrosion Cracking (SCC)
Chloride Stress Corrosion Cracking
Stainless Steel Corrosion
Corrosion of Piping
Corrosion Process
Surface Coatings for Corrosion
Corrosion Resistant Material
Bi- Metallic Corrosion.Galvanic Corrosion
Intergranular Corrosion
Intergranular Corrosion of Stainless Steel Tubes
Corrosion Resistant Stainless Steel Tube
Corrosion Resistance of Stainless Steel Tubes
Seawater Resistance of Stainless Steel Tubes
Corrosion Mechanism in Stainless Steel Tube
ASTM A262 Intergranular Corrosion Test IGC
ASTM E112 Standard Test Methods for Determining Average Grain Size
Methods of minimizing chloride stress corrosion cracking
| 