Selection of stainless steel for handling nitric acid (HNO3)
Nitric acid is strongly oxidising and promotes the resistance of stainless steel to corrosion.
Generally stainless steel are resistant to corrosion in nitric acid. Nitric acid is used in the chemical passivation of stainless steel.
Commercially concentrated acid is around 65 wt % (sg = 1.40). Higher concentrations obtained by removing water, which can involve the use of sulphuric acid, which has a high affinity for water.
Corrosion resistance of stainless steel
Nitric acid is strongly oxidising and attacks most metals but due to its powerful oxidising nature, it promotes the resistance of stainless steel to corrosion. Generally stainless steel are resistant to corrosion in nitric acid over a wide range of concentration and temperature. The 'helpful' oxidising properties of nitric acid are used in the chemical passivation of stainless steel.
The iso-corrosion diagram 0.1mm/year lines for the 304 and 316 types coincide (purple).
(The broken line represents the boiling point)
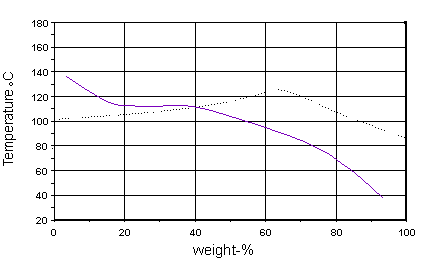
This shows that the 304 types can be used over a wide range of concentration and temperature, up to 95%, for storage applications. The 304 types are preferable to 316 types for nitric acid applications however. This is an exception to the 'general rule' for stainless steels where the 316 types are normally found to be more corrosion resistant than 304 types.
Over 95% concentration, aluminium alloys should be considered OR 4% silicon stainless steels.
Any additional chlorides or fluorides in nitric acid may increase corrosion rates by pitting.
Risk of localised corrosion in concentrated acids
Localised attack at grain boundaries (IC) can occur in hot concentrated nitric acid.
This can occur in the heat-affected-zone (HAZ) of welds.
Prolonged heating in a range of around 600-800 degC, followed by exposure to concentrated nitric acid, can also result in localised attack, due to the precipitation of the brittle "intermetallic" (iron-chromium) compounds (sigma phase).
Avoiding localised attack in concentrated acid
To avoid the risk of localised corrosion, especially where post weld heat treatment is impractical, the low carbon, 304L types should be considered.
Solution heat treatment (1050 -1100 degC followed by fast cooling) on the standard carbon 304 type can be considered as an alternative. These treatments should also re-dissolve any sigma formed.
Compostions of 304L type have been used with silicon, phosphorous & sulphur limited to very low residual levels to improve the resistance in hot concentrated nitric acid.
Uses for nitric acid with stainless steels
Nitric acid is widely used in the chemical 'passivation' of stainless steels.
Material Performance in Nitric acid, HNO3
| Conc. % |
0.5 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
5 |
5 |
5 |
5 |
5 |
10 |
10 |
10 |
10 |
20 |
20 |
20 |
| Temp. °C |
250 |
20 |
50 |
100 =BP |
20 |
50 |
100 =BP |
150 |
290 |
20 |
50 |
101 =BP |
145 |
20 |
50 |
103 =BP |
| Grade or type of alloy: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Carbon steel |
|
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
| 13 Cr |
|
0 |
1 |
2 |
0 |
1 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
0 |
1 |
2 |
2 |
0 |
1 |
2 |
| 317L |
|
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
2 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
2 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
| 317LM / 1.4439 |
|
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
2 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
2 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
| 904L |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
2 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
2 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
| Sanicro 28 |
|
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
|
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
0 |
|
|
| 254 SMO |
|
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
|
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
|
|
|
| 654 SMO |
|
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
|
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
|
|
|
| SAF 2304 |
|
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
|
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
|
|
|
| SAF 2205 |
|
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
|
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
|
|
|
| SAF 2507 |
|
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
|
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
|
|
|
| Titanium (CP Ti) |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
| Conc. % |
20 |
30 |
30 |
30 |
30 |
50 |
50 |
50 |
50 |
50 |
60 |
60 |
60 |
60 |
65 |
65 |
| Temp. °C |
120 |
20 |
70 |
106 =BP |
120 |
20 |
70 |
90 |
110 |
117 =BP |
20 |
60 |
100 |
121 =BP |
20 |
60 |
| Grade or type of alloy: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Carbon steel |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
| 13 Cr |
2 |
0 |
1 |
2 |
2 |
0 |
1 |
1ig |
2 |
2 |
0 |
1 |
2 |
2 |
0 |
1 |
| 317L |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0ig |
1ig |
1ig |
0 |
0 |
1ig |
1ig |
0 |
0 |
| 317LM / 1.4439 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0ig |
1ig |
1ig |
0 |
0 |
1ig |
1ig |
0 |
0 |
| 904L |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0ig |
0ig |
1ig |
0 |
0 |
0ig |
1ig |
0 |
0 |
| Sanicro 28 |
|
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
0 |
0 |
0ND |
0ND |
0ND |
|
|
|
|
0 |
0 |
| 254 SMO |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1ig |
|
|
|
|
0 |
0 |
| 654 SMO |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| SAF 2304 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0ig |
|
|
|
|
0 |
0 |
| SAF 2205 |
|
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
0 |
0 |
0ND |
0ND |
0ND |
|
|
|
|
0 |
0 |
| SAF 2507 |
|
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
0 |
0 |
0ND |
0ND |
0ND |
|
|
|
|
0 |
0 |
| Titanium (CP Ti) |
1 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
| Conc. % |
65 |
65 |
65 |
65 |
80 |
80 |
80 |
80 |
90 |
90 |
90 |
94 |
97 |
99 |
99 |
99 |
| Temp. °C |
70 |
90 |
121 =BP |
175 |
20 |
50 |
80 |
106 =BP |
20 |
80 |
94 =BP |
30 |
25 |
25 |
40 |
84 =BP |
| Grade or type of alloy: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Carbon steel |
2 |
2 |
2 |
|
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
| 13 Cr |
1 |
1ig |
2 |
|
0 |
1 |
2 |
2 |
0 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
| 317L |
0 |
1ig |
1ig |
|
0 |
0 |
1ig |
1ig |
0 |
2 |
2 |
0 |
|
1 |
2 |
2 |
| 317LM / 1.4439 |
0 |
1ig |
1ig |
|
0 |
0 |
1ig |
1ig |
0 |
2 |
2 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
2 |
2 |
| 904L |
0 |
0ig |
1ig |
|
0 |
0 |
1ig |
1ig |
0 |
1ig |
2 |
0 |
|
1 |
2 |
2 |
| Sanicro 28 |
0 |
0ig |
0ig |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 254 SMO |
0 |
0ig |
1ig |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 654 SMO |
|
|
1ig |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| SAF 2304 |
0 |
0ig |
1ig |
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| SAF 2205 |
0 |
0ig |
1ig |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| SAF 2507 |
0 |
0ND |
1ig |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Titanium (CP Ti) |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
Symbol clarification
These corrosion tables use a number of symbols, having the following meanings:
| Symbol |
Description |
| 0 |
Corrosion rate less than 0.1 mm/year. The material is corrosion proof. |
| 1 |
Corrosion rate 0.1—1.0 mm/year. The material is not corrosion proof, but useful in certain cases. |
| 2 |
Corrosion rate over 1.0 mm/year. Serious corrosion. The material is not usable. |
| p, P |
Risk (severe risk) of pitting and crevice corrosion. |
| c, C |
Risk (Severe risk) of crevice corrosion. Used when there is a risk of localised corrosion only if crevices are present. Under more severe conditions, when there is also a risk of pitting corrosion, the symbols p or P are used instead. |
| s, S |
Risk (Severe risk) of stress corrosion cracking. |
| ig |
Risk of intergranular corrosion. |
| BP |
Boiling solution. |
| ND |
No data. (Used only where there are no actual data to estimate the risk of localised corrosion instead of p or s). |
Releated References:
Selection of Stainless Steel fo Handling Sulphur Dioxide SO2 and Sulphur Trioxide SO3
Selection of Stainless Steel for Handling Phosphoric Acid H3PO4
Selection of Stainless Steel for Handling Hydrofluoric Acid HF
Selection of Stainless Steel for Handling Citric Acid C3H4OH (COOH)3
Selection of Stainless Steel for Handling Ammonia NH3
Selection of Stainless Steel for Handling Chlorine Cl2 and Chlorine Dioxide ClO2
Selection of Stainless Steels For Handling Hydrochloric Acid HCl
Selection of Stainless Steel for Handling Sulphuric Acid H2SO4
Selection Stainless Steel for Handling Sodium Hydroxide NaOH
Selection of stainless steels for handling acetic acid (CH3COOH)
Selection of stainless steels for handling sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl)
Selection of stainless steels for handling nitric acid (HNO3)
NACE MR 0175/ISO 15156 for Corrosion Resistant Alloys for Sulphide Service
Selection of stainless steels in water supply and waste water treatment
|
