Nimonic 80A UNS N07080 2.4952 2.4631 Alloy
Nimonic Alloy 80A is a nickel-chromium alloy similar to Nimonic alloy 75 but made precipitation hardenable by additions of aluminium and titanium. Alloy 80A has good corrosion and oxidation resistance and high tensile and creep-rupture properties at temperature to 815ºC (1500ºF). Alloy 80a is used for gas-turbine components (blades, rings, discs), bolts, tube supports in nuclear generators, exhaust valves in internal combustion engines and has many other offshore/marine, automotive and electrical applications. Nickel-chromium alloy strengthened by additions of titanium and aluminum. The alloy is used for high temperature, high strength applications.
Machinability, Conventional machining techniques used for iron based alloys may be used. This alloy does work-harden during machining and has higher strength and "gumminess" not typical of steel. Heavy duty machining equipment and tooling should be used to minimize chatter or work-hardening of the alloy ahead of the cutting.
Most any commercial coolant may be used in the machining operations. Water-base coolants are preferred for high speed operations such as turning, grinding, or milling. Heavy lubricants work best for drilling, tapping, broaching or boring. Turning: Carbide tools are recommended for turning with a continuous cut. High-speed steel tooling should be used for interrupted cuts and for smooth finishing to close tolerance. Tools should have a positive rake angle.
Forming, This alloy has good ductility and may be readily formed by all conventional methods. Because the alloy is stronger than regular steel it requires more powerful equipment to accomplish forming. Heavy-duty lubricants should be used during cold forming. It is essential to thoroughly clean the part of all traces of lubricant after forming as embrittlement of the alloy may occur at high temperatures if lubricant is left on.
Cutting speeds and feeds are in the following ranges: For High-Speed Steel Tools For Carbide Tooling Depth Surface Feed Depth Surface Feed of cut speed in inches of cut speed in inches inches feet/min. per rev. inches feet/min. per rev. 0.250" 25-35 0.030 0.250" 150-200 0.020 0.050" 50-60 0.010 0.050" 325-375 0.008 Drilling: Steady feed rates must be used to avoid work hardening due to dwelling of the drill on the metal. Rigid set-ups are essential with as short a stub drill as feasible. Heavy-duty, high-speed steel drills with a heavy web are recommended. Feeds vary from 0.0007 inch per rev. for holes of less than 1/16" diameter, 0.003 inch per rev. for 1/4" dia., to 0.010 inch per rev. for holes of 7/8"diameter. Milling: To obtain good accuracy and a smooth finish it is essential to have rigid machines and fixtures and sharp cutting tools. High-speed steel cutters such as M-2 or M-10 work best with cutting speeds of 30-40 feet per minute and feed of 0.004"-0.006" per cutting tooth. Grinding: The alloy should be wet ground and aluminum oxide wheels or belts are preferred.
Welding, The commonly used welding methods work well with this alloy. Matching alloy filler metal should be used. If matching alloy is not available then the nearest alloy richer in the essential chemistry (Ni, Co, Cr, Mo) should be used. All weld beads should be slightly convex. It is not necessary to use preheating. Surfaces to be welded must be clean and free from oil, paint or crayon marking. The cleaned area should extend at least 2" beyond either side of a welded joint. Gas-Tungsten Arc Welding: DC straight polarity (electrode negative) is recommended. Keep as short an arc length as possible and use care to keep the hot end of filler metal always within the protective atmosphere.
Shielded Metal-Arc Welding: Electrodes should be kept in dry storage and if moisture has been picked up the electrodes should be baked at 600 F for one hour to insure dryness. Current settings vary from 60 amps for thin material (0.062" thick) up to 140 amps for material of 1/2" and thicker. It is best to weave the electrode slightly as this alloy weld metal does not tend to spread. Cleaning of slag is done with a wire brush (hand or powered). Complete removal of all slag is very important before successive weld passes and also after final welding. Gas Metal-Arc Welding: Reverse-polarity DC should be used and best results are obtained with the welding gun at 90 degrees to the joint. For Short-Circuiting-Transfer GMAW a typical voltage is 20- 23 with a current of 110-130 amps and a wire feed of 250-275 inches per minute. For Spray-Transfer GMAW voltage of 26 to 33 and current in the range of 175-300 amps with wire feed rate of 200-350 inches per minute are typical. Submerged-Arc Welding: Matching filler metal, the same as for GMAW, should be used. DC current with either reverse or straight polarity may be used. Convex weld beads are preferred.
Heat Treatment, Solution anneal at 1975 F for 8 hours and air cool. The hold at 1300 F for 16 hours to precipitation harden and air cool.
Forging, Forging may be done in the temperature range of 2150 F to 1800 F.
Hot Working, Hot working may be done in the temperature range of 2150 F to 1800 F. Avoid hot working at temperatures of 1000 F to 1800 F.
Cold Working, Cold forming may be done using standard tooling although plain carbon tool steels are not recommended for forming as they tend to produce galling. Soft die materials (bronze, zinc alloys, etc.) minimize galling and produce good finishes, but die life is somewhat short. For long production runs the alloy tool steel ( D-2, D-3) and high-speed steels (T-1, M-2, M-10) give good results especially if hard chromium plated to reduce galling. Tooling should be such as to allow for liberal clearances and radii. Heavy duty lubricants should be used to minimize galling in all forming operations. Bending of sheet or plate through 180 degrees is generally limited to a bend radius of 1 T for material up to 1/8" thick and 2 T for material thicker than 1/8".
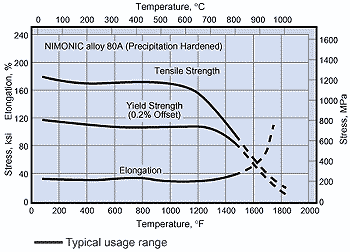
Typical Mechanical Properties
Specifications and Designation: UNS N07080 BS 3076 (NA 20), HR1, HR201, HR401, HR601 ASTM B 637 DIN 17742, 17754 Werkstoff Nr. 2.4952, 2.4631 WL Nr. 2.4631 AFNOR NC 20TA AECMA Pr EN 2188-2191, 2396, 2397
Chemical Composition |
| Weight % |
Ni |
Cr |
Ti |
Al |
C |
Si |
Cu |
Fe |
Mn |
Co |
B |
Zr |
S |
| Alloy 80A |
Bal |
18.0-21.0 |
1.8-2.7 |
1.0-1.8 |
0.10 max |
1.0 max |
0.2 max |
3.0 max |
1.0 max |
2.0 max |
0.008 max |
0.15 max |
0.015 max |
Nimonic 80A Physical properties:
Nimonic 80A minimum mechanical properties in the room temperature:
Status |
|
|
Elongation
A5 % |
Nimonic 80A |
930 |
620 |
20 |
Typical Mechanical Properties Alloy 80A
Rupture Strength (1000 h) |
| Temperature |
ksi |
MPa |
| 595°C / 1100°F |
94 |
650 |
| 650°C / 1200°F |
73 |
500 |
| 705°C / 1300°F |
51 |
350 |
| 760°C / 1400°F |
32 |
220 |
| 815°C / 1500°F |
16 |
110 |
Alloy 80a was Precipitation Hardening
|
