Speeds and Feeds for Turning Stainless Steel
Traditionally high speed tool steel have been used for most turning operations, but carbide tipped tool are now also used. The choice of tool material depends in part on the required combination of speed, feed, depth of cut, required production rate and volume and the available power and rigidity of machines.
Single point turning
Cutting Point Angles

End and side relief angles must be ground flat, without any concavity. Concave faces reduce the support at the cutting edge and can result in chipping or breaking.
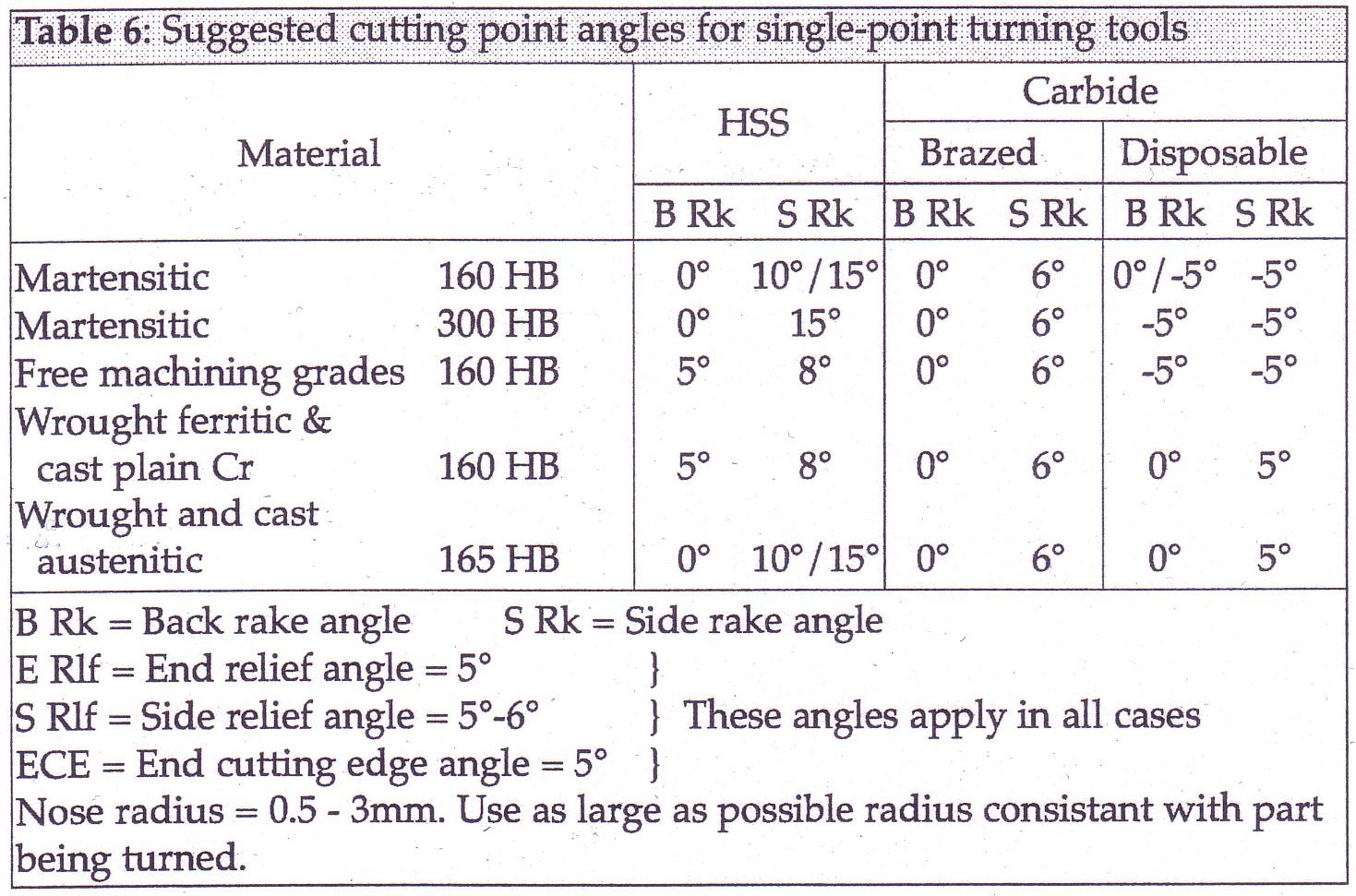
Feeds and Speeds
The surface speeds shown for the different tool types are at the set depths of cut and feed shown. If depth of cut and feed are increased, the speed must be reduced. Alternatively for increased speeds, reduce the depth of cut and feed. For austenitic steel (e.g. 304, 1.4301) the depth of cut must however always undercut the induced work hardened layer, so increase in speed must be carefully limited. Similarly, it is important to leave enough steel on the surface when completing the last roughing cut to enable sufficient finishing cut depth. Where this is impractical, a carbide tool used at high speed, low feed and a shallow depth of cut is an option.
Too high a speed can result in tool tip burning. Too low a speed can result in chip build-up on the cutting edge. As a general rule, when there are cutting problems adjust the speed first and then, where necessary, the feed second.
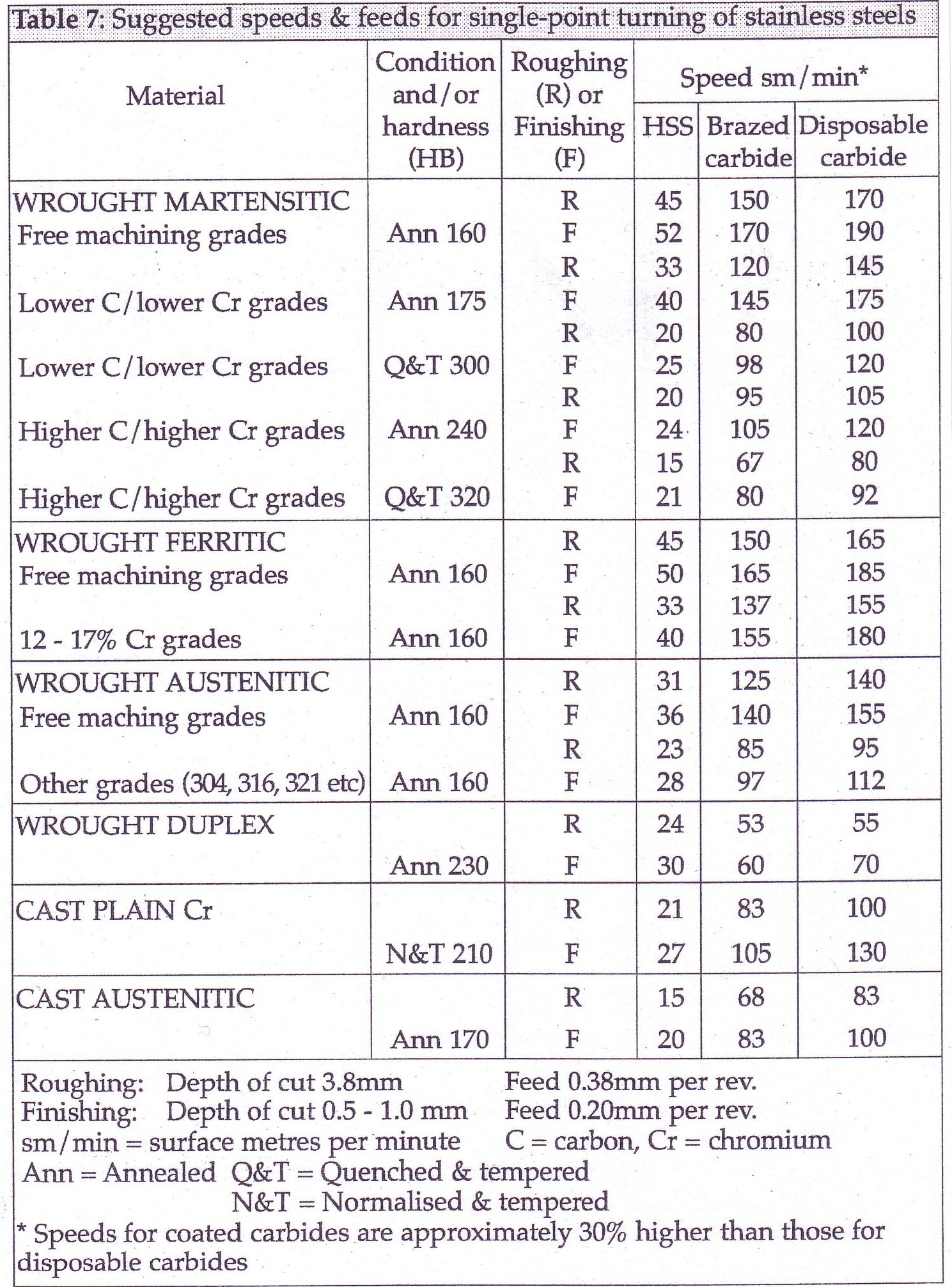
Form tool turning
Cutting Tool Angles
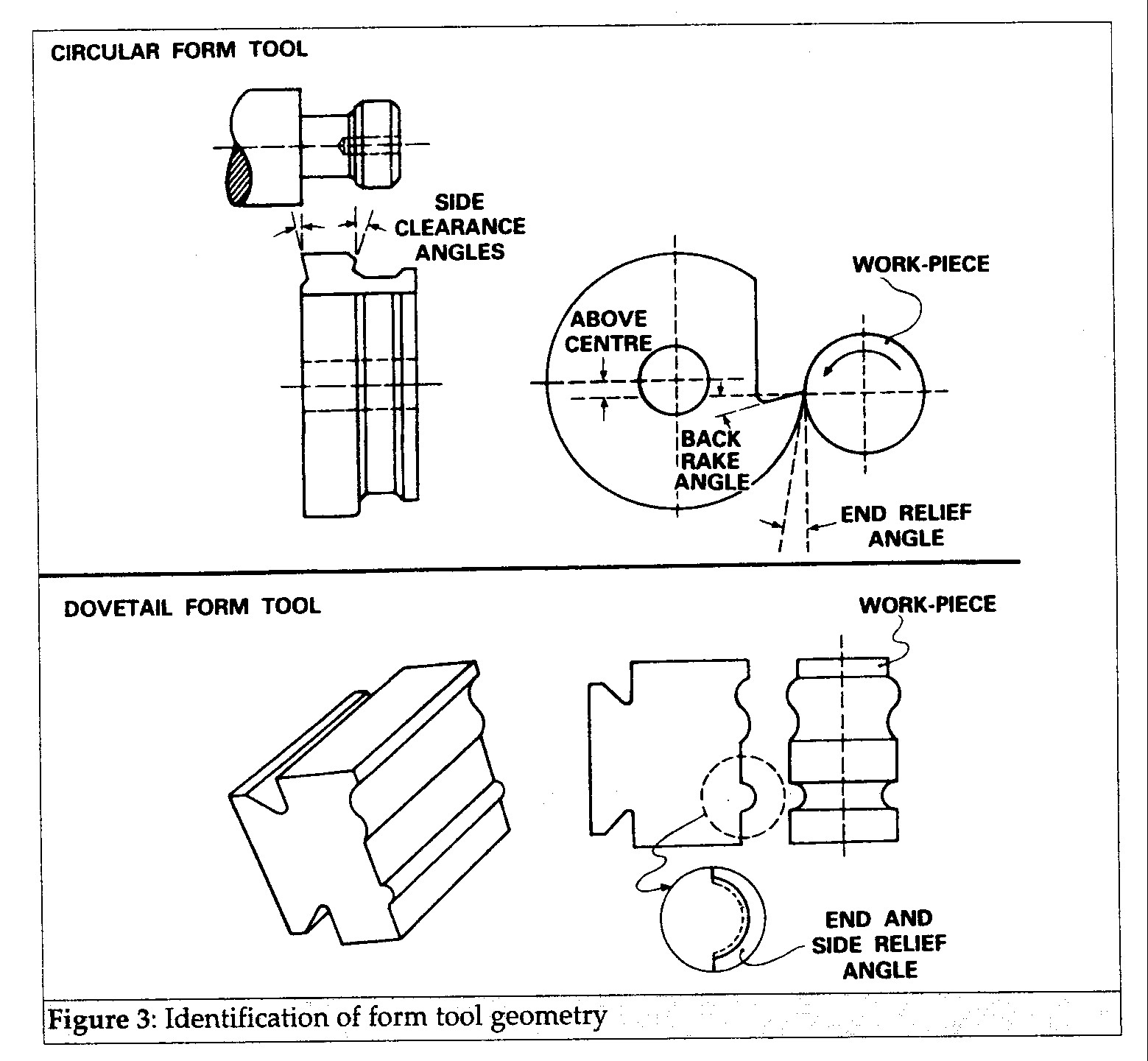
Back rake angles should be between 4 and 10 degrees. The smaller angles suit secondary cuts in multi-cut operations. The larger angles suit single cut operations or the primary cuts of multiple cut operations. Top face and back rake angles should have a smooth polished finish to avoid chip flow problems that can result in poor finish or overheating due to poor access of coolant to the cutting edges.
Side relief and clearance angles should be between 1 and 5 degrees. The deeper the cut, the larger the angle. 'Above centre' distances should about 3mm.
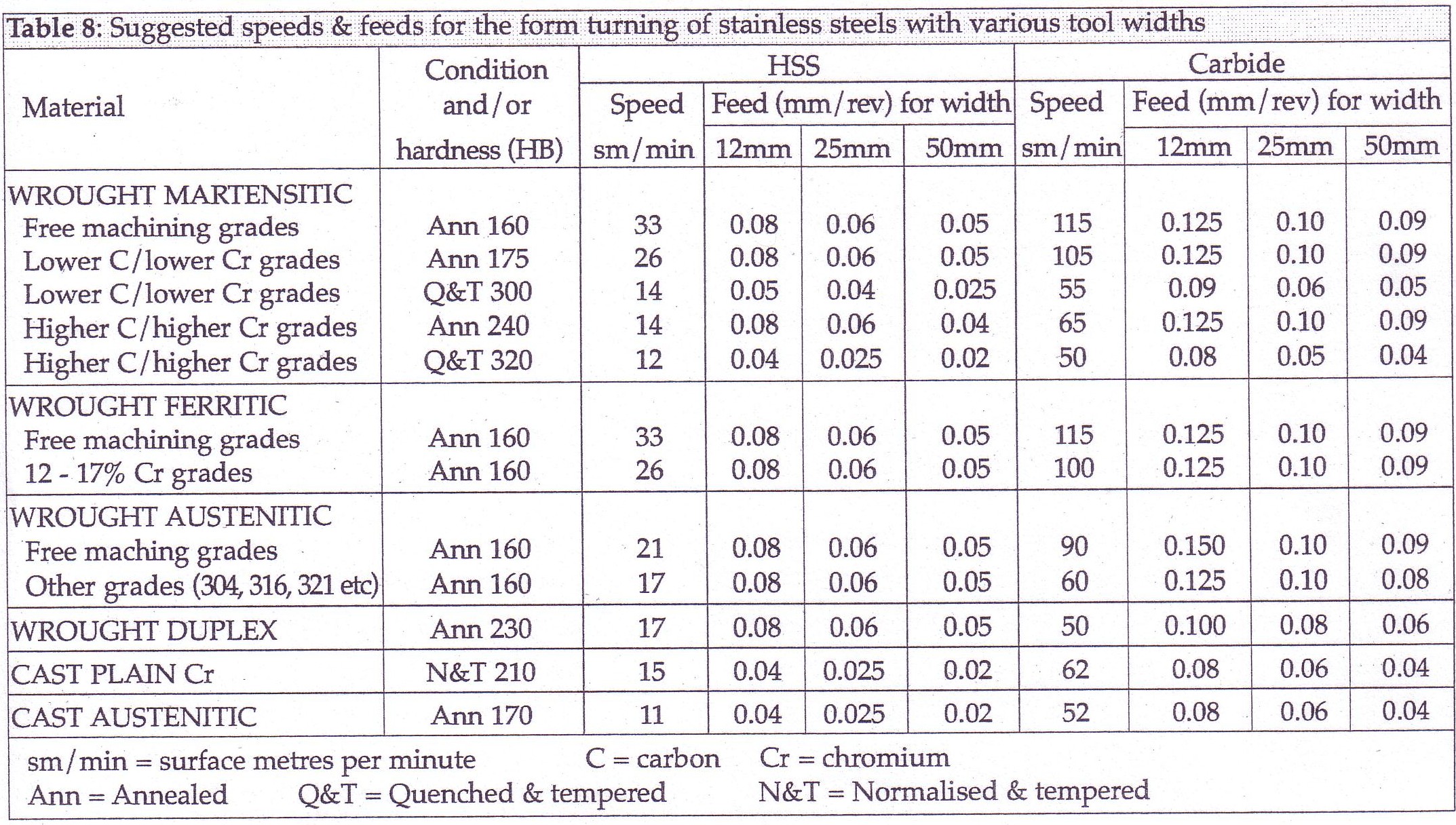
Feeds and Speeds
Form turning stainless steel should allow sufficient material to be removed to avoid surface work hardening problems. This applies to both primary and secondary cuts in multi-cut operations. Feed must be maintained as the tool enters the work-piece.
For form tool turning deep or complex shapes, slower speeds should be considered. The flow of cutting fluid (coolant) must be carefully controlled to ensure that a consistent, large flow volume is delivered to the cutting edges at all times during form tool turning of stainless steel.
Cut-off (parting-off) tool turning
Cutting Tool Angles
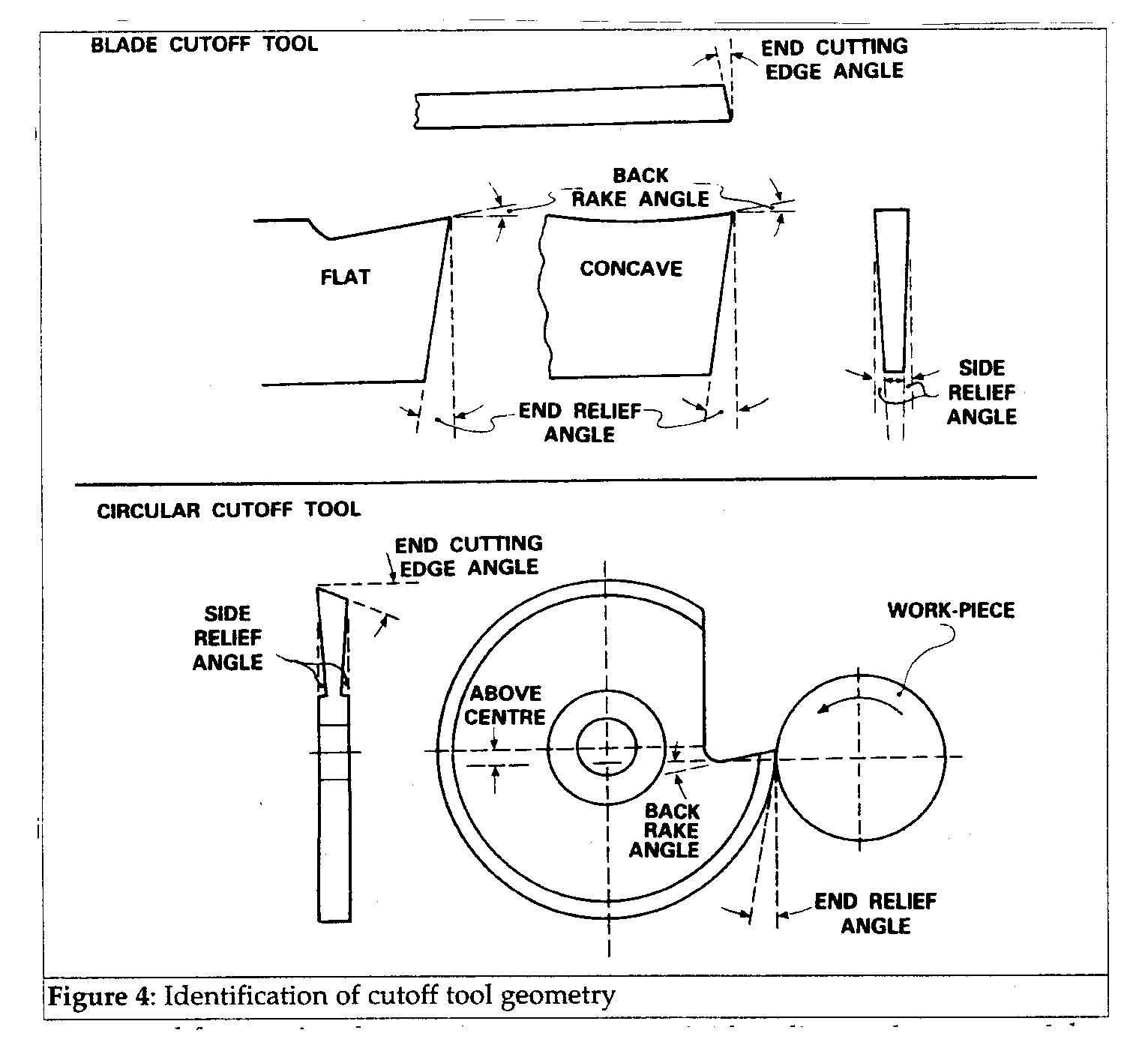
Either blade or circular tools can be used.
Circular tools are more rigid and provide a better heat sink capacity than blade cutters and so are generally preferred for parting-off stainless steel, where sufficient cut depth is allowed by the tool geometry. Circular tools are also better for interrupted cuts as the tool passes through details like drilled holes.
Back rake angles should be between 6 and 10 degrees.
End relief angles should be between 7 and 10 degrees and should be ground flat to provide maximum support for the cutting edge. Side relief angles should be between 2 and 3 degrees. For large cut depths larger the side relief angles may be needed to avoid tool seizure.
Circular tools require an end cutting edge angle relief, usually between 10 and 15 degrees. The angle should be reduced as the depth of cut increases on larger diameter work-pieces to around 5 degrees, to avoid tool deflection. These smaller angles can result in some burr being left which may have to be trimmed off with a second cut. 'Above centre' distances should about 3mm.
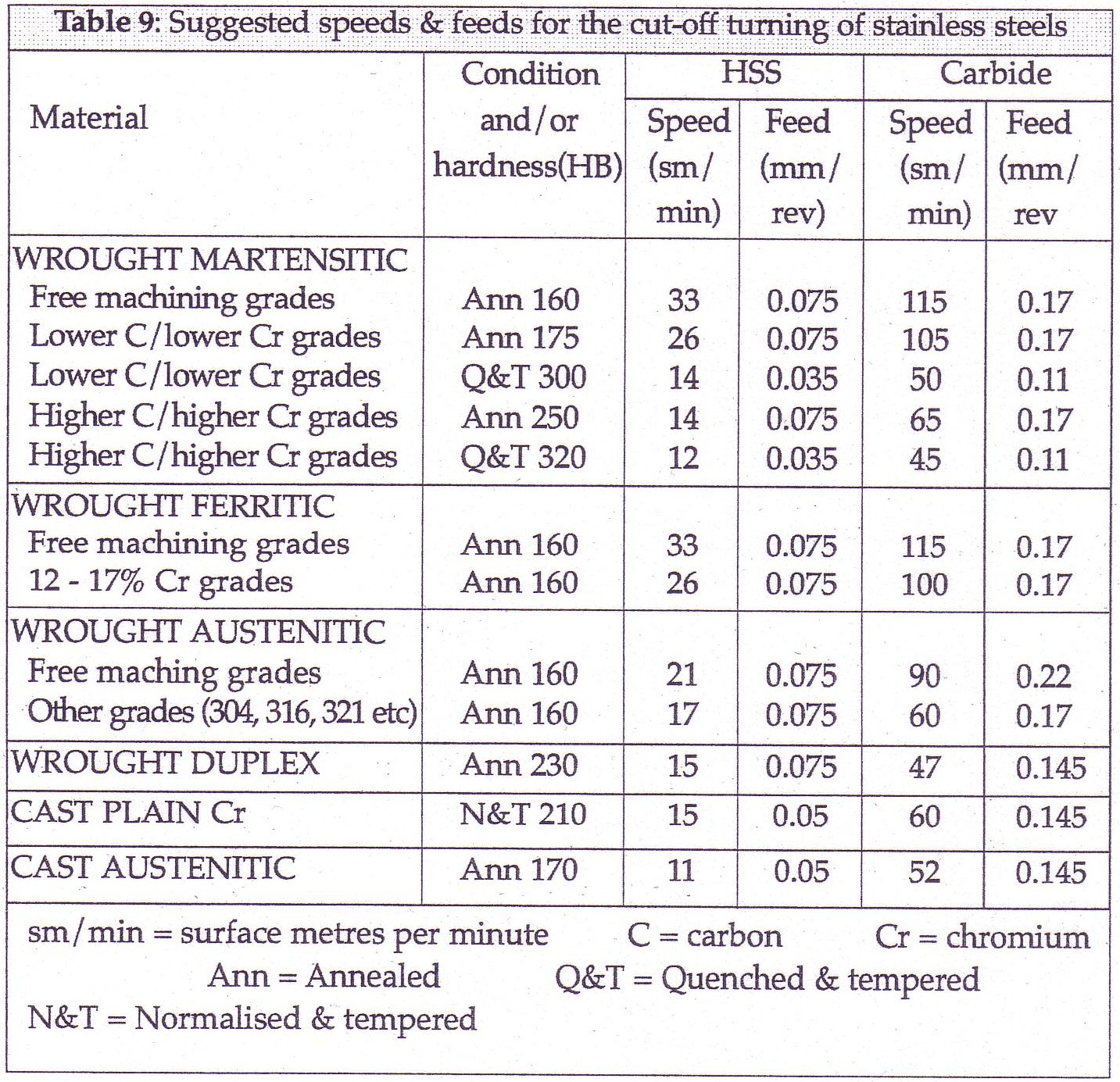
Feeds and Speeds
Related References:
Screw Thread Limits Table
UNC UNF Threads Per Inch TPI Threads Per Inch
Wood Screw Pilot Hole Sizes Table
Standard NPT National Pipe Thread Tap Drill Sizes Table
ASTM ISO Metric Thread Sizes and Tap Drill Table
Tapping Drill Size and Clearance Drill Size for Metric Threads
Standard Number Drill Sizes Table
Metric Thread Size Tap Drill Table
Standard Tap Drills Clearance Holes Table
Standard Letter Drill Sizes Table
Standard Drill Sizes Decimal Equivalents Table
Socket Head Cap Screw Sizes Dimension Table
SAE Grade ASTM Bolt Identify Marks Mechanical Properties
Steel Bolt Torque Specifications Table
Finished Hex Nut Dimensions
Heavy Hex Nut Dimensions Table
Standard ANSI Type B Flat Washer Sizes
Circumferential Speeds for High Speed Twist Drill Table
|
