HDG Hot Dip Galvanized Bond Strength
Below the name of each layer in the figure above (magnified cross-section of hot-dip galvanized coating) appears its respective hardness, expressed by a Diamond Pyramid Number (DPN). The DPN is a progressive measure of hardness; the higher the number, the greater the hardness. Typically, the Gamma, Delta and Zeta layers are harder than the underlying steel. The hardness of these inner layers provides exceptional protection against coating damage by abrasion. The Eta layer is quite ductile, providing the coating with some impact resistance.
Good bonding between reinforcing steel and concrete is essential for reliable performance of reinforced concrete structures. When protective coatings on steel are used, it is essential to ensure that these coatings do not reduce bond strength. Studies of the bonding of galvanized and black steel bars to Portland Cement concrete have been investigated.
The results of these studies indicate:
- Development of the bond between steel and concrete depends on age and environment.
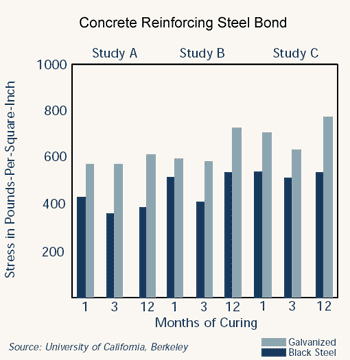
- The fully developed bond strength of galvanized and black deformed bars is the same. In the chart below, the bond strength of galvanized bars is greater than for similar black bars.
Bond Strength Test
The bond of the hot-dip galvanized reinforcing bar to the concrete can be tested according to ASTM A 944. The bond strength relies heavily on the deformation of the bar and not as much on the actual bond between the zinc and the concrete. For plain bars with no deformation, the bond between the zinc and the concrete becomes very important. Pullout strength of hot-dip galvanized reinforcing steel has been tested many times, and the values of bond strength are equivalent to, or better than, black steel bond strength, as illustrated in the chart above.
The galvanized coating is adherent to the underlying steel on the order of several thousand pounds per square inch (psi). Other coating typically offer adhesion rated at several hundred psi at best. Hardness, ductility and adherence combine to provide the galvanized coating with unmatched protection against damage caused by rough handling during transportation to and/or at the job site, as well as in service. The toughness of the galvanized coating is extremely important since barrier protection is dependent upon the integrity of the coating.
Related References:
1. About Zinc
2. About Hot-Dip Galvanizing
3. HDG Hot-Dip Galvanizing Last Time
4. Cost of Galvanized Steel
5. Selection of Zinc Coatings
6. Zinc Coatings-Galvanized|Electrogalvanized|Galvanneal|Galfan
7. Physical Properties of HDG Hot-Dip Galvanized
8. HDG Hot-Dip Galvanized Abrasion Resistance Resistance to Mechanical Damage
9. Hot-Dip Galvanized Corrosion Protection and the Zinc Patina
10. HDG Hot-Dip Galvanized High Temperature Exposure
11. HDG Hot-Dip Galvanized Surface Reflectivity
12. HDG Hot Dip Galvanized Coating Structure
13. HDG Hot Dip Galvanized Bond Strength
14. HDG Hot Dip Galvanized Coating Uniformity
15. HDG Hot Dip Galvanized Coating Thickness
16. Powder Coating Hot Dipped Galvanized Steel
17. Painting Hot-Dippped Galvanized Steel
18. Painting Hot-Dipped Galvanized Steel Surface Preparation
19. Surface Coatings for Corrosion
20. Hot-Dip Galvanizing Surface Preparation
21. Hot-Dip Galvanizing Galvanizing
22. Hot-Dip Galvanizing Inspection
23. Characteristics of Zinc
24. Hot-Dip Galvanizing Performance in Atmosphere
25. Hot-Dip Galvanizing in Atmosphere Time to First Maintenance
26. Hot-Dip Galvanizing Performance in Soil
27. Soil Corrosion Data for Corrugated Steel Pipe
28. Hot-Dip Galvanizing Performance in Water
29. Cause of Zinc Corrosion
30. Corrosion of Zinc Coated Steel in Selected Natural Fresh Water
31. Corrosion of Zinc and Zinc Coated Steel in Sea Water
32. Corrosion of Zinc Coating in Industrial and Domestic Water
33. Concrete Corrosion of Hot Dip Galvanizing
34. Concrete corrosion resistance of hot dip galvanized reinforcing
35. Removal of Forms Concrete Corrosion
36. Zinc Reaction in Concrete Corrosion
37. Concrete Corrosion References
38. Hot-Dip Galvanizing Performance in Chemical Solutions
39.Hot-Dip Galvanizing Performance in Contact with Other Metals
40. Hot-Dip Galvanizing Performance in contact with Treated Wood
41. Hot-Dip Galvanizing Performance in contact with Food
42. Hot-Dip Galvanizing Performance in Extreme Temperature
|
