HDG Hot-Dipped Galvanized Last Time
Hot-Dipped Galvanized HDG is used to protect steel from corrosion in a variety of environments, including air, water, chemicals, and soil applications. Galvanized steel’s performance in each of these applications is dependent upon a unique set of corrosion variables. The information in the subsequent pages details what variables impact the coating’s performance and how long it will last in the given environment. To learn more, view the Specifier’s Guide.
Most commonly, hot-dip galvanized steel applications are in the atmosphere or open air. In atmospheric applications, hot-dip galvanized steel naturally exposed to wet and dry cycles which are crucial to the development of a series of films on the zinc surface known as the patina. The patina is stable and non-reactive unless exposed to aggressive chloride or sulfides, and is a key component to galvanizing’s long life.
Numbers of independent and industry tests of galvanized steel sample have been performed over decade in industrial, urban,and marine environment to determine the time to maintenance in each environment.
It is important to note the data represented on this site about galvanized steel’s performance is based on actual performance in the field, and not on accelerated testing methods. Manufacturers of many other corrosion protection systems use these tests to claim their products perform as well as hot-dip galvanized steel based on accelerated testing, namely salt spray tests. However, salt spray tests do not allow the zinc coating to go through the natural wet and dry cycles required to form the zinc patina.
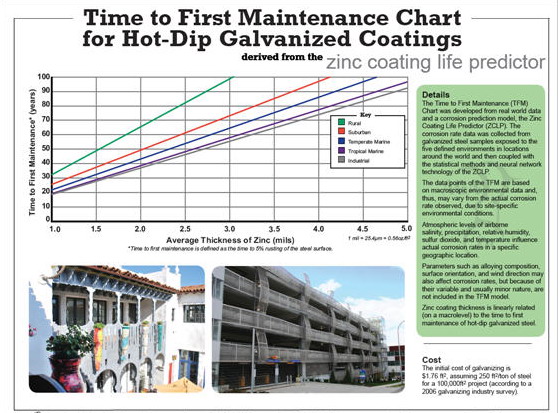
Related References:
1. About Zinc
2. About Hot-Dip Galvanizing
3. HDG Hot-Dip Galvanizing Last Time
4. Cost of Galvanized Steel
5. Selection of Zinc Coatings
6. Zinc Coatings-Galvanized|Electrogalvanized|Galvanneal|Galfan
7. Physical Properties of HDG Hot-Dip Galvanized
8. HDG Hot-Dip Galvanized Abrasion Resistance Resistance to Mechanical Damage
9. Hot-Dip Galvanized Corrosion Protection and the Zinc Patina
10. HDG Hot-Dip Galvanized High Temperature Exposure
11. HDG Hot-Dip Galvanized Surface Reflectivity
12. HDG Hot Dip Galvanized Coating Structure
13. HDG Hot Dip Galvanized Bond Strength
14. HDG Hot Dip Galvanized Coating Uniformity
15. HDG Hot Dip Galvanized Coating Thickness
16. Powder Coating Hot Dipped Galvanized Steel
17. Painting Hot-Dippped Galvanized Steel
18. Painting Hot-Dipped Galvanized Steel Surface Preparation
19. Surface Coatings for Corrosion
20. Hot-Dip Galvanizing Surface Preparation
21. Hot-Dip Galvanizing Galvanizing
22. Hot-Dip Galvanizing Inspection
23. Characteristics of Zinc
24. Hot-Dip Galvanizing Performance in Atmosphere
25. Hot-Dip Galvanizing in Atmosphere Time to First Maintenance
26. Hot-Dip Galvanizing Performance in Soil
27. Soil Corrosion Data for Corrugated Steel Pipe
28. Hot-Dip Galvanizing Performance in Water
29. Cause of Zinc Corrosion
30. Corrosion of Zinc Coated Steel in Selected Natural Fresh Water
31. Corrosion of Zinc and Zinc Coated Steel in Sea Water
32. Corrosion of Zinc Coating in Industrial and Domestic Water
33. Concrete Corrosion of Hot Dip Galvanizing
34. Concrete corrosion resistance of hot dip galvanized reinforcing
35. Removal of Forms Concrete Corrosion
36. Zinc Reaction in Concrete Corrosion
37. Concrete Corrosion References
38. Hot-Dip Galvanizing Performance in Chemical Solutions
39.Hot-Dip Galvanizing Performance in Contact with Other Metals
40. Hot-Dip Galvanizing Performance in contact with Treated Wood
41. Hot-Dip Galvanizing Performance in contact with Food
42. Hot-Dip Galvanizing Performance in Extreme Temperature
|
