HDG Hot Dip Galvanized Coating Uniformity
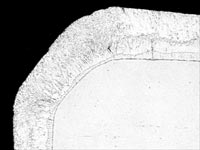
The galvanizing process naturally produces coating that are at least as thick at the corners and edges as the coating on the rest of the article. As coating damage is most likely to occur at the edges, this is where added protection is needed most. Brush- or spray-applied coatings have a natural tendency to thin at the corners and edges. The figure below is a photomicrograph showing a cross-section of a corner of a galvanized piece of steel.
Because the galvanizing process involves total immersion of the material, all surface are coated. Galvanizing provides protection on both exterior and interior surfaces of hollow structures. Hollow structures that are painted (but not galvanized) have no corrosion protection on the inside.
The inspection process for galvanized items is simple and fast and requires minimal labor. This is important because the inspection process required to assure the quality of many brush- and spray-applied coatings is highly labor-intensive and uses expensive skilled labor.
Galvanizing takes place in a factory regardless of weather or humidity conditions. Most brush- and spray-applied coatings depend upon proper weather and humidity conditions for correct application. This dependence on atmospheric conditions often translates into costly construction delays. The galvanizer’s ability to work in any type of weather allows a higher degree of assurance of on-time delivery. Working under these circumstances, galvanizing can be completed quickly and with short lead times. A turnaround time of two or three days for galvanizing is common.
Related References:
1. About Zinc
2. About Hot-Dip Galvanizing
3. HDG Hot-Dip Galvanizing Last Time
4. Cost of Galvanized Steel
5. Selection of Zinc Coatings
6. Zinc Coatings-Galvanized|Electrogalvanized|Galvanneal|Galfan
7. Physical Properties of HDG Hot-Dip Galvanized
8. HDG Hot-Dip Galvanized Abrasion Resistance Resistance to Mechanical Damage
9. Hot-Dip Galvanized Corrosion Protection and the Zinc Patina
10. HDG Hot-Dip Galvanized High Temperature Exposure
11. HDG Hot-Dip Galvanized Surface Reflectivity
12. HDG Hot Dip Galvanized Coating Structure
13. HDG Hot Dip Galvanized Bond Strength
14. HDG Hot Dip Galvanized Coating Uniformity
15. HDG Hot Dip Galvanized Coating Thickness
16. Powder Coating Hot Dipped Galvanized Steel
17. Painting Hot-Dippped Galvanized Steel
18. Painting Hot-Dipped Galvanized Steel Surface Preparation
19. Surface Coatings for Corrosion
20. Hot-Dip Galvanizing Surface Preparation
21. Hot-Dip Galvanizing Galvanizing
22. Hot-Dip Galvanizing Inspection
23. Characteristics of Zinc
24. Hot-Dip Galvanizing Performance in Atmosphere
25. Hot-Dip Galvanizing in Atmosphere Time to First Maintenance
26. Hot-Dip Galvanizing Performance in Soil
27. Soil Corrosion Data for Corrugated Steel Pipe
28. Hot-Dip Galvanizing Performance in Water
29. Cause of Zinc Corrosion
30. Corrosion of Zinc Coated Steel in Selected Natural Fresh Water
31. Corrosion of Zinc and Zinc Coated Steel in Sea Water
32. Corrosion of Zinc Coating in Industrial and Domestic Water
33. Concrete Corrosion of Hot Dip Galvanizing
34. Concrete corrosion resistance of hot dip galvanized reinforcing
35. Removal of Forms Concrete Corrosion
36. Zinc Reaction in Concrete Corrosion
37. Concrete Corrosion References
38. Hot-Dip Galvanizing Performance in Chemical Solutions
39.Hot-Dip Galvanizing Performance in Contact with Other Metals
40. Hot-Dip Galvanizing Performance in contact with Treated Wood
41. Hot-Dip Galvanizing Performance in contact with Food
42. Hot-Dip Galvanizing Performance in Extreme Temperature
|
