Zirconium 702 705 ASME Allowable Stress
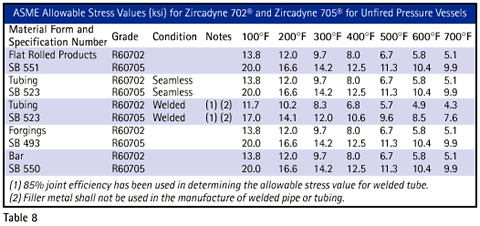
Zirconium alloys are approved for use in the construction of pressure vessels designed to the ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code.Zirconium 705 requires a stress relief heat treatment within 14 days after welding. Table 8 lists the allowable stress values for Zirconium alloys per the ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code, Section II part D,1997 addended edition.
Fatigue Limit Zirconium alloys exhibit a fatigue limit behavior (stress below which failure will not occur)similar to most ferrous alloys. At ambient temperature, however,Zirconium alloys exhibit somewhat higher ultimate tensile strength in the direction transverse to the rolling direction.
This properties of higher strengths in the transverse direction is unlike most ferrous alloys and is due to the orientation and directional properties of the hexagonal close-packed crystalline structure of alpha zirconium opposed to the body-centered cubic crystalline structure of alpha iron. This increase in strength in the transverse direction is more significant at stresses above the fatigue limit.
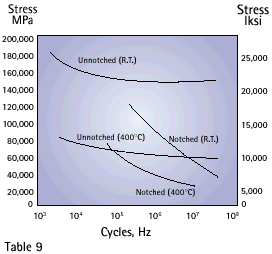
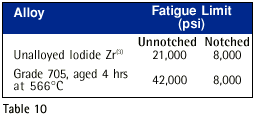
Table 9 shows the S-N flexure fatigue curves for both notched and unnotched round zirconium specimens.The theoretical elastic stress-concentration factor,K t , is 3.5 and was derived from Neuber plots. The strength reduction factor,K f ,defined as the ration of unnotched to notched fatigue strength is 2.6 at room temperature and 1.6 at 400 °C. Table 10 provides fatigue data for unalloyed iodide zirconium and Zirconium 705.
 ASTM B658 ASTM B523 ZR702 ZR705 Pipe
ASTM B658 ASTM B523 ZR702 ZR705 Pipe
Related References:
Zirconium Zirkonium Zircone
Corrosion Resistance of Zirconium
Physical Properties of Zirconium
Zirconium 702 705 Mechanical Properties
Zirconium 702 705 ASME Allowable Stress
|
