Heat Radiation
The transfer of heat energy by radiation can occur in a vacuum, unlike conduction and convection. Heat radiation is the same form of wave energy transfer as light, radio, and x-ray wave energy. The rate of emmission of heat energy is related to the temperature difference, the distance between the surfaces, and the emissivity of the surface. Bright reflective surfaces have the lowest emissivity values.
Radiation is heat transfer by the emission of electromagnetic waves which carry energy away from the emitting object. For ordinary temperature (less than red hot), the radiation is in the infrared region of the electromagnetic spectrum. The relationship governing radiation from hot objects is called the Stefan-Boltzmann law.
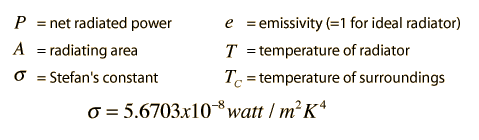
|
